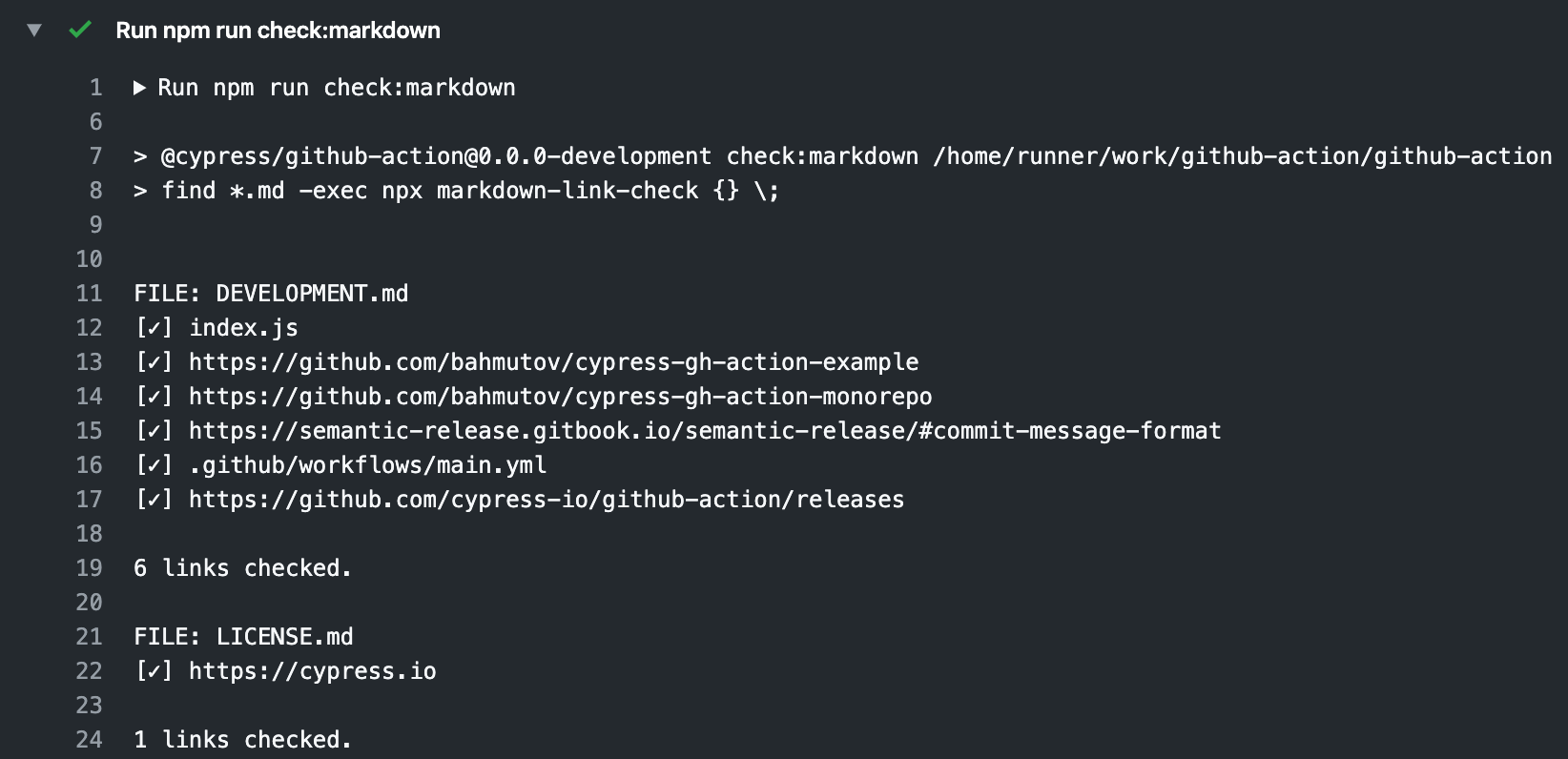
As the official Markdown documentation states, Markdown does not provide any special syntax for tables. Instead it uses HTML syntax. But there exist Markdown syntax extensions which provide additional syntax for creating simple tables. Markdown is a an easy-to use, lightweight markup language with syntax that maximizes readability and ergonomics while writing and makes publishing for the web super easy. It was created by John Gruber and Aaron Swartz, and is now used on thousands of websites and inside some of the world's most popular open source projects.
HackMD offers a great unified Markdown editor/preview which is familiar and well-suited to our needs. Our meeting records have improved a lot over a short period and as a result we are able to be better accountable to each other as a team. You just start writing Markdown text, save the file with the.md extension and then you can toggle the visualization of the editor between the code and the preview of the Markdown file; obviously, you can also open an existing Markdown file and start working with it. To switch between views, press Ctrl+Shift+V in.
Weblog Publishing
Markdown Monster can also publish your Markdown directly to your Weblog. If your blog supports WordPress, MetaWeblog, Jekyll or Medium, you can publish your documents with one click. You can also edit and republish, or download existing posts and even convert existing posts from HTML to Markdown.
Extensible via .NET
We also wanted to make sure the editor is highly extensible, so you can add custom features of your own. Markdown Monster includes an addin model that makes it easy to build extensions that let you hook into the UI, the editor behavior and the publishing process. We also provide useful Scripting and Text Templating addins that let you automate many tasks without creating an addin. Find out more about creating an addin with .NET.
What our Users say
We work hard at building an editor that you love to use, and that provides you with the features you need. Your feedback matters and we'd love to hear your suggestions and see you get involved.
But don't take our word for it - here is what some of our users are saying about Markdown Monster:
Want to share your excitement for Markdown Monster? Tweet to @markdownmonstr and tell us how Markdown Monster improves your world.Markdown is a lightweight markup language for adding formatting elements to plain text. IntelliJ IDEA recognizes Markdown files, provides a dedicated editor with highlighting, completion, and formatting, and shows the rendered HTML in a live preview pane.
Create a new Markdown file
By default, IntelliJ IDEA recognizes any file with the .md or .markdown extension as a Markdown file.
Right-click a directory in the Project tool window Alt+1 and select New | File.
Alternatively, you can select the necessary directory, press Alt+Insert, and then select File.
Enter a name for your file with a recognized extension, for example: readme.md.
The Markdown editor provides several basic formatting actions in the toolbar:
: Bold
: Strikethrough
: Italic
: Code
: Decrease heading level
: Increase heading level
: Convert an inline link to a reference link
You can use the preview pane to see the rendered HTML.
There is also completion for links to files in the current project, for example, if you need to reference source code, images, or other Markdown files.
Code blocks
To insert a fenced code block, use triple backticks (```) before and after the code block. If you specify the language for the code block, by default, the Markdown editor injects the corresponding language. This enables syntax highlighting and other coding assistance features for the specified language: code completion, inspections, and intention actions.
Disable coding assistance in code blocks
If your code blocks are not meant to be syntactically correct, you may want to disable code injection and syntax errors in code blocks.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Languages & Frameworks | Markdown.
Configure the following options:
Disable automatic language injection in code fences Do not inject any coding assistance for code blocks. Hide errors in code fences Do not check the syntax for errors. Click OK to apply the changes.
Diagrams
The Markdown editor can render diagrams defined with Mermaid and PlantUML. This is disabled by default and requires the corresponding Markdown extensions.
Enable diagram support
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Languages & Frameworks | Markdown.
Enable either Mermaid or PlantUML under Markdown Extensions.
After IntelliJ IDEA downloads the relevant extensions, click OK to apply the changes.
HTML preview
By default, the Markdown editor shows a preview pane next to it for rendered HTML code based on the Markdown file. You can use or in the top right corner of the Markdown editor to show only the editor or the preview pane.
The scrollbars in the editor and in the preview pane are synchronized, meaning that the location in the preview pane corresponds to the location in the source. To disable this, click in the top right corner of the Markdown editor.
To split the editor and preview pane horizontally (top and bottom) instead of the default vertical split, in the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Languages & Frameworks | Markdown, and then select Split horizontally under Editor and Preview Panel Layout.
Custom CSS
IntelliJ IDEA provides default style sheets for rendering HTML in the preview pane. These style sheets were designed to be consistent with the default UI themes. You can configure specific CSS rules to make small presentation changes (for example, change the font size for headings or line spacing in lists) or you can provide an entirely new CSS to better match your expected output (for example, if you want to replicate the GitHub Markdown style).
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Languages & Frameworks | Markdown.
Configure the settings under Custom CSS:
Select Load from URI to specify the location of a custom CSS file.
Select Add CSS rules rules to enter specific CSS rules that you want to override.
Reformat Markdown files
IntelliJ IDEA can format Markdown files with proper line wrappings, blank lines, and indentation. For more information, see Reformat and rearrange code.
From the main menu, select Code | Reformat Code or press Ctrl+Alt+L.
IntelliJ IDEA formats the contents according to the code style settings for Markdown files.
Configure Markdown code style settings

In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Editor | Code Style | Markdown.
Markdown code style settings include the following:
Configure the options for breaking lines.
| Hard wrap at | Specify at which column to put a line break. IntelliJ IDEA shows a vertical line at the specified column and breaks lines between words, not within words. |
| Wrap on typing | Add line breaks as you type. Disable this option to add line breaks only when IntelliJ IDEA performs formatting. |
| Visual guides | Show an additional vertical line at the specified column. |
Configure the options for nesting text blocks and alignment within a block.
| Use tab character | Use the tab character for indentation. Disable this option to use spaces for indentation. |
| Smart tabs | Nest blocks with tabs and align with spaces. Disable this option to use only tabs and replace spaces that fit the specified tab size with tabs. |
| Tab size | Specify the number of spaces to render in place of one tab character. |
| Indent | Specify the number of spaces used for each indentation level. |
| Continuation indent | Specify the number of spaces used for continuing the same text block. |
| Keep indents on empty lines | Retain tabs and spaces on empty lines. By default, this option is disabled and IntelliJ IDEA removes tabs and spaces if there is nothing else on that line. |
Md Markdown Language
Set the maximum and minimum number of blank lines to keep for various text elements.
| Around header | Before and after chapter headings. |
| Around block elements | Before and after code blocks. |
| Between paragraphs | Between two adjacent paragraphs. |
Specify which elements should have exactly one space.
| Between words | Remove extra spaces between words. |
| After header symbol | Remove extra spaces or add a missing space between the header symbol and the header title. |
| After list marker | Remove extra spaces or add a missing space between the list item marker and the list item text. |
| After blockquote marker | Remove extra spaces or add a missing space between the block quote marker and the text of the block quote. |
Productivity tips
Customize highlighting for Markdown
IntelliJ IDEA highlights various Markdown elements according to the color scheme settings.
In the Settings/Preferences dialog Ctrl+Alt+S, select Editor | Color Scheme | Markdown.
Select the color scheme, accept the highlighting settings inherited from defaults, or customize them as described in Configuring colors and fonts.
Navigate in a large Markdown file
Md Markdown File
Use the Structure tool window Alt+7 or the File Structure popup Ctrl+F12 to view and jump to the relevant headings.
Github Markdown Guide
Markdown does not have dedicated syntax for commenting out lines. However, it is possible to emulate a comment line using a link label without an address, like this:
There must be a blank line before the link label.
Put the caret at the line that you want to comment out and press Ctrl+/.
This will add a link label with the commented out text in parentheses and a blank line before it if necessary. Press the same shortcut to uncomment.
Md Markdown Syntax
